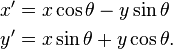3 回复 | 直到 15 年前
|
|
1
22
这取决于你如何定义
但如果顺时针测量,则第二个是正确的: |
|
|
2
27
|
|
|
3
1
这是从我自己的向量库中提取的。 |
推荐文章

|
Fyodor · 在C中使用sin和cos计算数学表达式不正确? 1 年前 |

|
Cjmarkham · 基于已知斜边和相邻的[闭合]获得θ 1 年前 |
|
|
Quiche31 · 符号反三角函数并不总是返回期望的分数 2 年前 |
|
|
Jack Wild · 三名JS直接在摄像机前获得地面位置 7 年前 |
|
|
urukh · Arduino波发生器 7 年前 |
|
|
Michael K. · 如何以java度求反余弦 7 年前 |