|
|
1
4
对我来说,直截了当(如果难看的话)的解决方案是使用EXISTS和notexists子句: ……等等。在这个例子中,我们要求的是服用药物474但没有服用药物234的人。显然,你可以根据你的需要用and和ORs对从句进行分组。
|
|
|
2
1
我不知道这在大型表中会有什么效果(我想这会非常糟糕,因为日期比较通常非常昂贵),但这里有一个方法应该可以工作。它相对冗长,但很容易针对不同的布尔情况进行修改。 例1:
|
|
|
3
1
|
|
|
4
0
请原谅任何错误,但我认为这样做是可行的(在T-SQL中):
现在它不需要一个联盟来完成,但为了可读性,我认为这是最简单的考虑到你的条件。也许这会把你引向正确的方向。 |
|
|
5
0
这会满足你的要求。最后的IN语句是非常不言自明的。 |
|
|
6
0
我没有现成的测试数据来进行测试,但我认为您可以做如下操作:
|

|
7
0
我可能会从类似的方向来处理这个问题。它很灵活。 |
|
|
8
0
这可以通过将“药物需求”转换成某种形式的临时表来简化。这将允许使用任何数量的“好”和“坏”药物进行查询。我下面的内容可以实现为存储过程,但是如果不是这样的话,有很多复杂的选项可用。 分解步骤: 弗斯特 第二 ,对于已经和在一起的每一组“目标”药物,设置一个这样的临时表(这是SQL Server语法,Postgres应该有类似的内容):
计算两个值:
@好的药物,你希望病人服用的药物数量
我故意忽略了时间标准,因为您没有详细介绍它们,但它们应该很容易添加(尽管我希望这不是著名的遗言)。 进一步的优化可能是可能的,但很大程度上取决于数据和其他可能的标准。 每次传球。你也许可以将“药物集”扩展到你正在检查的每个药物集中,但我不愿意尝试 没有一些重要的数据来测试它的代码。 */ |
|
|
9
0
给出的答案似乎都不管用。我想实现的模式是: ((药物234=正确,药物474=正确,药物26=错误)或 (药品395=假,药品791=假,药品371=真)
这个查询是有效的,但是非常难看。我还怀疑,一旦我有了一个拥有1亿人的生产数据库,它的速度会非常慢。我能做些什么来简化/优化这个查询吗? |
|
|
10
0
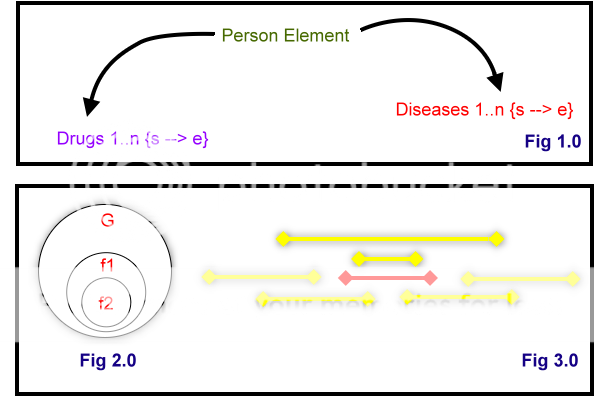
首先,三个表(人、药、病)如图1.0所示: 一个人可以拥有 倍数 毒品和多种毒品 疾病 . 每种药物和疾病都有一个开始日期&结束日期。 因此,我首先将三个表反规范化为一个表(table\u dn),因此: 如果需要,这个非标准化的表可以是临时表,而不管表现在包含了图2.0所示的所有全局数据集(表示为G)。 从我对你的描述的理解来看,我基本上可以看到一个两层过滤器。 过滤器1 这个过滤器只是一组布尔值 组合 ,如您在问题描述中所述。如: 过滤器2 这个过滤器比第一个稍微复杂一点,它是日期范围标准。图3.0显示了该日期范围 . 黄色表示以多种方式跨越的记录日期:
现在黄枣期可以是药物期或疾病期,也可以是两者的结合期。
当然,根据你的确切问题,这两个过滤器可能需要反过来(例如,先f2,然后f1)。
|

|
Johnny T · 基于当前值的SQL合并表[重复] 7 月前 |

|
John D · 需要为NULL或NOT NULL的WHERE子句 8 月前 |

|
ojek · 如何对SQL结果进行分组和编号? 8 月前 |
|
|
senek · 如何在PL/SQL中将选择结果(列)放入数组中 8 月前 |
|
|
Sax · 规范化Google表格(第一步) 8 月前 |
|
|
Jatin · 检索卷计数的动态sql抛出错误语法错误[关闭] 8 月前 |
|
|
Andrus · 如何在sql中查找第二个匹配项 8 月前 |